Introduction To Bladder Cancer Staging


Introduction to Bladder Cancer Staging
Bladder cancer, like other cancers, is measured in stages. The stages describe how far the cancer has spread. This key piece of information helps you and your doctor choose the best treatment for your unique case.

Two Types of Staging
There are two types of stages for bladder cancer – the clinical stage and the pathologic stage. The clinical stage is your doctor's informed opinion of how far your cancer has spread. This is based on tests such as imaging and biopsies. The pathologic stage is determined after you've had surgery to remove the cancer.

What Do the Stages Mean?
Doctors look at tumor size, whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes (clusters of disease fighting cells) near the bladder, and whether it has metastasized, or spread to organs or lymph nodes that aren't near the bladder.

Stage 0: Noninvasive Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer is noninvasive and remains in the inner lining of the bladder. It's the earliest stage and is treated more easily than later stages.
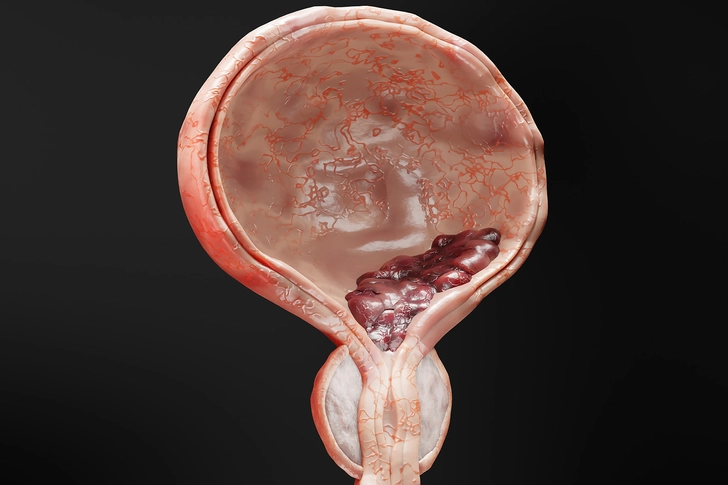
Stage I: Cancer in Connective Tissue
In stage I, cancer has spread to the connective tissue layer of the bladder but hasn't reached the muscle layer. Treatment may include surgery or localized therapies.

Stage II: Muscle Layer
The cancer has spread to the muscle layer of the bladder. Treatment may include surgery, possibly combined with chemotherapy or radiation.

Stage III: Spread to Surrounding Tissues
Stage III cancer has spread through the muscle layer to surrounding tissues or organs. Treatment often requires a combination of therapies.
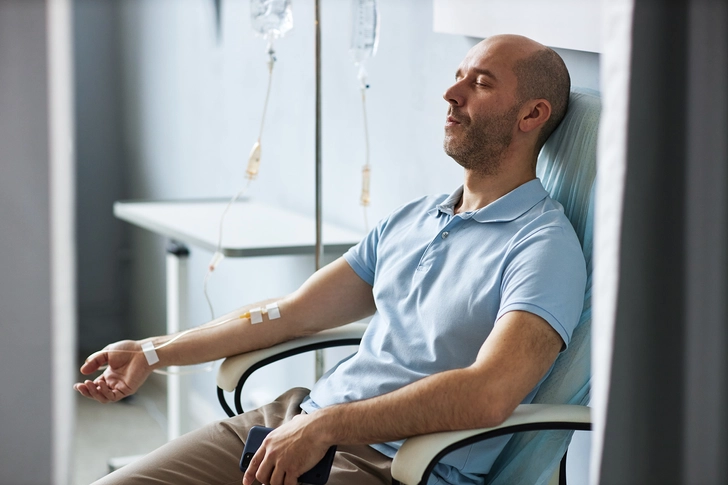
Stage IV: Distant Metastasis
In this stage, cancer has spread to distant sites like bones, liver, or lungs. This advanced stage often requires systemic treatments such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies.
Photo Credits:
1) Shidlovski/Shutterstock
2) CGN089/Shutterstock
3) MDV Edwards/Shutterstock
4) Mary Ann Zapalac/WebMD Ignite
5) ALIOUI MA/Shutterstock
6) ilusmedical/Shutterstock
7) Ana Krasavina/Shutterstock
8) SeventyFour/Shutterstock
American Cancer Society: “Bladder cancer stages.”
Cancer Research UK: “Invasive and advanced bladder cancer stages and grading.”
American Cancer Society: “Signs and symptoms of bladder cancer.”