- Overview
- Symptoms
- Causes & Risks
- Screening & Testing
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- How HIV Affects the Body
- Opportunistic Infections
- Complications
- Living With
- Dating & Relationships
- Support & Resources
- Prevention
- Appointment Prep
- View Full Guide
Understanding HIV Symptoms


Understanding HIV Symptoms
HIV symptoms can be subtle and easily overlooked. About 1 in 7 people with HIV don't know they have it. The only way to confirm an HIV infection is through testing. If you think you've been exposed, seek medical attention immediately. A doctor can prescribe post-exposure prophylaxis, which may prevent infection if taken within a day or two of exposure. Remember, early detection and treatment are crucial for managing HIV effectively.

Early Signs of HIV Infection
In the first eight weeks after infection, you may experience flu-like symptoms. These can include fever, muscle aches, fatigue, and night sweats. You might also notice swollen lymph nodes, a rash, or a sore throat. But some people don't have any symptoms at all. During this phase, the virus is multiplying rapidly in your body. If you're experiencing these symptoms and think you might have been exposed to HIV, it's important to get tested.

The Silent Phase of HIV
After the initial phase, HIV enters a chronic stage where you may not experience any symptoms for years. This doesn't mean the virus is inactive. Even without symptoms, HIV continues to attack your immune system, specifically your CD4 cells. Regular HIV testing is crucial. Don't let the absence of symptoms give you a false sense of security. Early detection and treatment can prevent the progression of HIV and protect your health.

Signs of Advanced HIV Infection
If left untreated, HIV can progress to AIDS in around 10 years. Early signs of AIDS may include persistently swollen lymph nodes. As the immune system weakens, you might experience rapid weight loss, fever or night sweats, extreme fatigue, and prolonged diarrhea. Skin rashes, mouth sores, and frequent infections are also common. If you have any of these symptoms, especially if you're at risk for HIV, seek medical attention immediately.
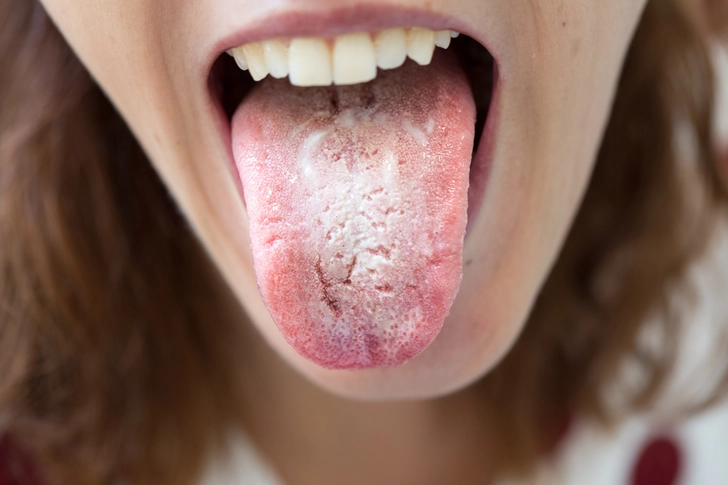
When Your Body Can't Fight Back
As HIV progresses to AIDS, your weakened immune system becomes vulnerable to opportunistic infections. You might develop a white coating in your mouth called thrush or experience breathing problems. Herpes infections can cause mouth, genital, or anal sores. Shingles, a painful nerve condition, may occur. Memory problems can also develop. These symptoms indicate severe immune system damage and require immediate medical attention.
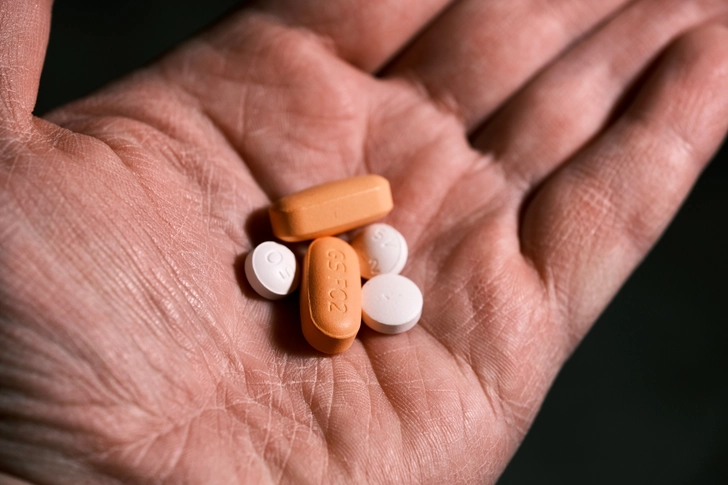
Taking Control of Your HIV Status
Early diagnosis and treatment of HIV can make a big difference in your health outcomes. Antiretroviral therapy can stop the destruction of your immune system, keep you healthy, and prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS. With proper treatment, people with HIV can live nearly as long as those without the virus. Regular testing is key, especially if you're more likely to get it.
PHOTO CREDITS:
Slide 1: New Africa/Shutterstock
Slide 2: baranq/Shutterstock
Slide 3: blurAZ/Shutterstock
Slide 4: Olena Yakobchuk/Shutterstock
Slide 5: sruilk/Shutterstock
Slide 6: Showtime.photo/Shutterstock
SOURCES:
Avert: "Symptoms and Stages of HIV Infection," "When to Get Tested for HIV?"
HIV.gov: "How Can You Tell If You Have HIV?" "How Do You Get HIV?"
University of California San Francisco: "HIV Signs and Symptoms."
CDC: "Information about Acute HIV Infection and PrEP," "PEP," "About HIV/AIDS."
AIDS info: "HIV Prevention."
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services/AIDS Info: "HIV Overview."
World Health Organization: "HIV/AIDS."
UCSF Health: "AIDS Signs and Symptoms."
Winchester Hospital: "Symptoms of AIDS."