- Overview
- Symptoms
- Causes & Risks
- Screening & Testing
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- How HIV Affects the Body
- Opportunistic Infections
- Complications
- Living With
- Dating & Relationships
- Support & Resources
- Prevention
- Appointment Prep
- View Full Guide
Understanding the CD4:CD8 Ratio Test

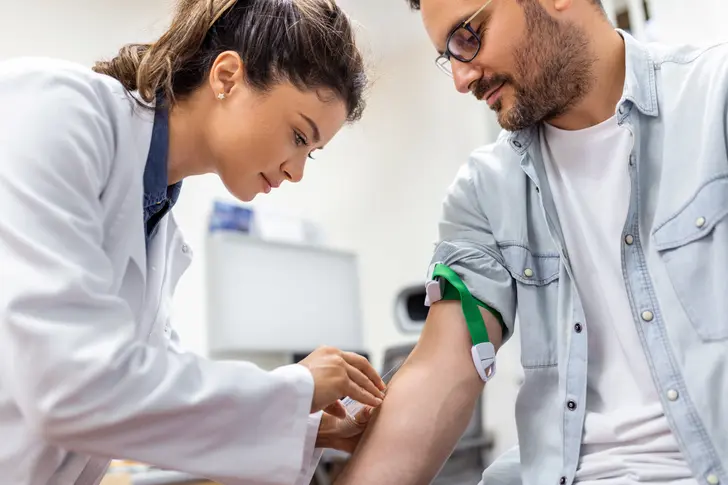
Understanding the CD4:CD8 Ratio Test
The CD4:CD8 ratio test measures two types of white blood cells crucial for your immune system. It's mainly used to monitor HIV infections but can also help with other conditions, such as mononucleosis or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. This test provides valuable insights into your immune system's strength and helps doctors tailor treatment plans for various health issues.
The Role of CD4 and CD8 Cells
CD4 cells coordinate immune responses by signaling other cells to attack invaders. CD8 cells directly attack and kill infected or cancerous cells. In HIV infections, the virus targets CD4 cells, leading to a low CD4 count and an imbalanced ratio of CD4 and CD8 cells. If you have an HIV infection, your CD4:CD8 ratio test results can help your doctor know how active the virus is in your body and how you're responding to your medicine.
Normal Ranges of CD4 and CD8 Cells
A normal CD4 count typically ranges from 500 to 1,200 cells per milliliter of blood. If you have an HIV infection and your CD4 count falls below 200 cells per milliliter of blood, your doctor will likely diagnose you with AIDS. A CD4 count this low significantly increases your risk of developing life-threatening infections and cancer. A normal CD8 count generally ranges from 150 to 1,000 cells per milliliter of blood.

Interpreting Your CD4:CD8 Ratio Test Results
The CD4:CD8 ratio is calculated by dividing the CD4 count by the CD8 count. A normal ratio falls between 1 and 3. A ratio below 1 may suggest an untreated HIV infection, ineffective HIV treatment, or other health issues, such as anemia or multiple sclerosis. Your CD4:CD8 ratio may be higher than 3 if you have a serious bacterial infection, a viral infection (such as COVID-19), or some type of blood cancer.

CD4:CD8 Ratio Test in HIV Management
For HIV patients, the CD4:CD8 ratio test helps track treatment effectiveness and immune system recovery. A CD4 count above 500 cells per milliliter indicates controlled HIV infection. Regular testing every three to six months while on antiretroviral therapy helps doctors monitor progress. It may take years of consistent treatment for CD4 counts to return to normal levels.
PHOTO CREDITS:
Slide 1: Photoroyalty/Shutterstock
Slide 2: Arif biswas/Shutterstock
Slide 3: 3dMediSphere/Shutterstock
Slide 4: Aquarius Studio/Shutterstock
Slide 5: Studio Romantic/Shutterstock
SOURCES:
Cleveland Clinic: "White Blood Cells," "T Cells," "Lymphocytes," "Helper T cells," "Cytotoxic T cells."
Li, R. CD4 Count, StatPearls Publishing, 2023.
Journal of the International AIDS Society: "Elevation and persistence of CD8 T-cells in HIV infection: the Achilles heel in the ART era."
University of Rochester Medical Center: "CD4-CD8 Ratio."
MedlinePlus: "CD4 Lymphocyte Count."
aidsmap: "CD4/CD8 ratio," "Is the CD4/CD8 ratio a useful test for people with HIV?"
CDC: "Getting Tested for HIV."