Understanding Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
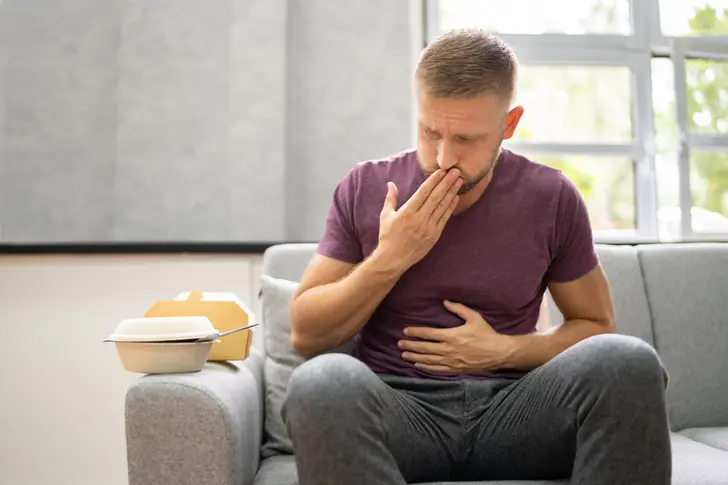


What Is Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis?
Acute severe ulcerative colitis is a complication of ulcerative colitis. It’s diagnosed when your disease flares and causes frequent bowel movements, bloody diarrhea, rapid heart rate, abdominal tenderness, fever, high levels of inflammation, bloating, and anemia. If you have it, you may need to be hospitalized depending on how severe your symptoms are.
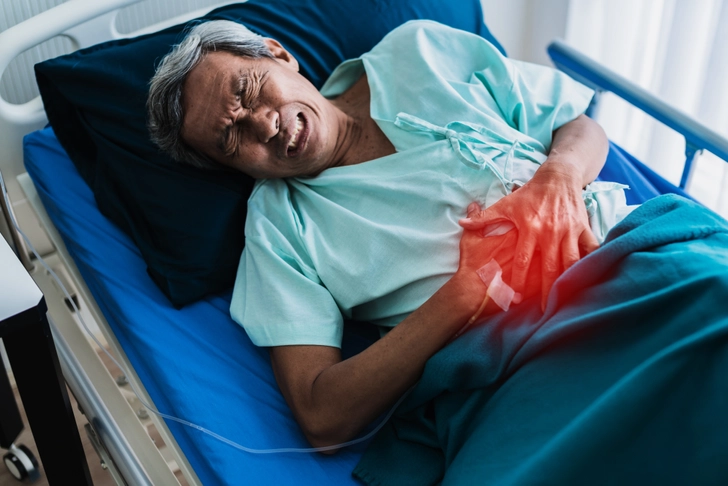

Hospitalization and Initial Treatment
People with acute severe ulcerative colitis are usually in the hospital for 4 to 12 days. Their treatment begins with diagnostic tests and intravenous fluids (IVs). Corticosteroids are usually used next, but they're not always effective.
When Corticosteroids Don't Work
If corticosteroids don't work within 3 to 5 days, you may be given immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or infliximab. If your symptoms still don’t get better, your doctor may suggest surgery to remove all parts of your colon (a colectomy).
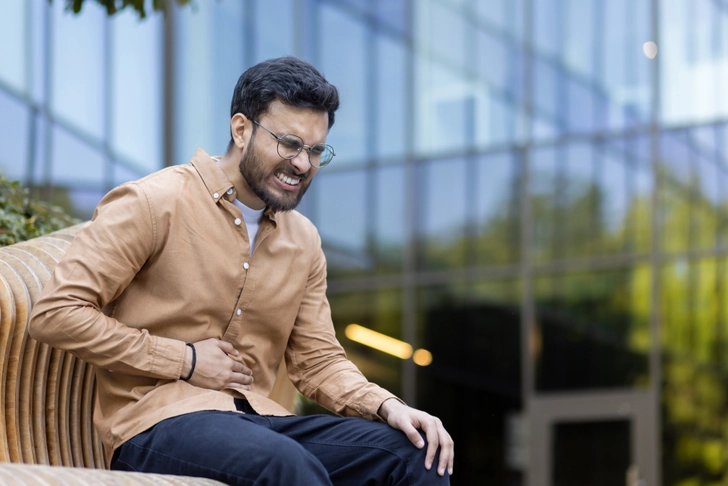

Risk Factors and Long-Term Outcomes
Acute severe ulcerative colitis is more common in men ages 15 to 35. It usually happens within the first year of your diagnosis. About 20% of patients may need a colectomy after their first hospitalization. This increases to 40% after multiple hospital visits. Older patients, especially those over 80, have a higher risk of death.
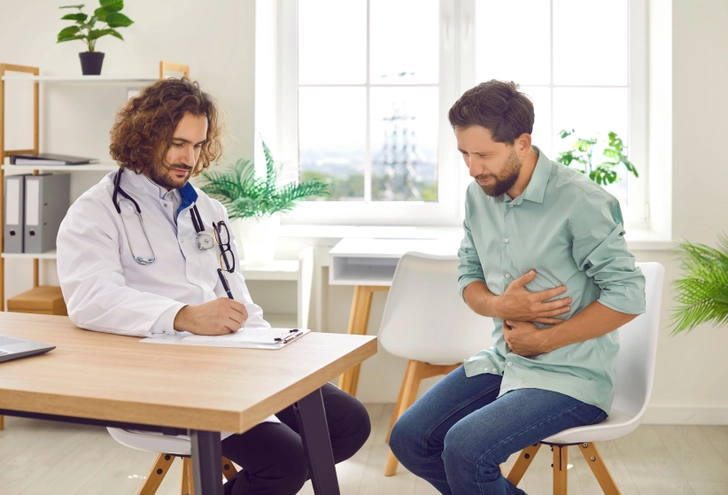

Making Informed Decisions for Your Health
Acute severe ulcerative colitis is a serious condition. It’s important for you to understand your options and get treated early. Make sure to educate yourself and communicate openly with your care team about any questions or concerns you may have.
PHOTO CREDITS:
01 - Andrey_Popov / Shutterstock
02 - WHYFRAME / Shutterstock
03 - luchschenF / Shutterstock
04 - voronaman / Shutterstock
05 - Studio Romantic / Shutterstock
SOURCES:
Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America.
Internal and Emergency Medicine: “Acute severe ulcerative colitis: management advice for internal medicine and emergency physicians.”
Gastroenterology: “American Gastroenterological Association Institute Clinical Guideline on the Management of Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis.”
Journal of Hospital Medicine: “Inpatient Management of Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis.”
Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology: “Optimal Management of Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis (ASUC): Challenges and Solutions.”
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease: “Acute severe ulcerative colitis: latest evidence and therapeutic implications.”
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology: “Tofacitinib for Biologic-Experienced Hospitalized Patients With Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Retrospective Case-Control Study.”
World Journal of Gastroenterology Pharmacology and Therapeutics: “Predictive factors for a severe clinical course in ulcerative colitis: Results from population-based studies.”
Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis: “Predicting the Individual Risk of Acute Severe Colitis at Diagnosis.”