- Overview
- Causes, Risks & Prevention
- Signs & Symptoms
- Tests & Diagnosis
- Your Lung Cancer Care Team
- Treatment
- Living With
- Remission & Recurrence
- Support & Resources
- Appointment Prep
- View Full Guide
What Is Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer?

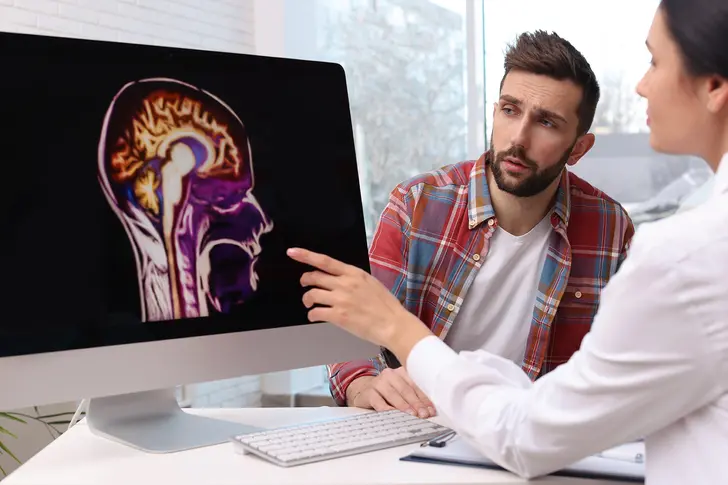
What Is Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer?
Stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most advanced stage of this type of lung cancer. At this stage, cancer has spread beyond the lungs to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver. This is also called metastatic lung cancer. Although it usually can't be cured, treatments can help manage symptoms, slow cancer growth, and improve quality of life.
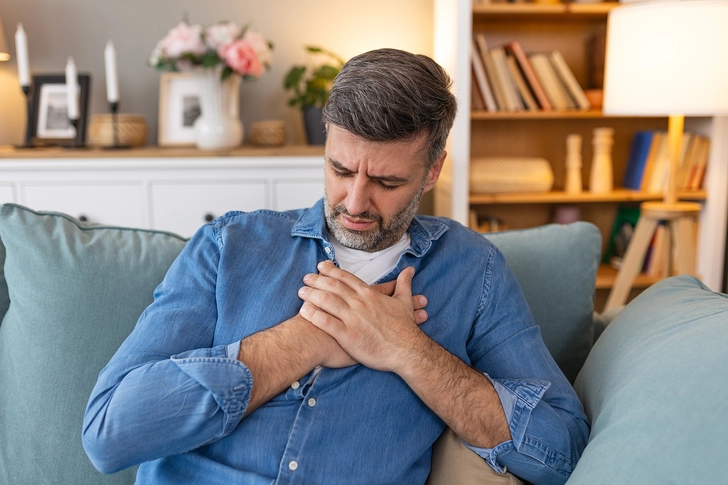

Common Symptoms of Stage IV NSCLC
Symptoms vary depending on where the cancer has spread. Common signs include persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, shortness of breath, and unexplained weight loss. As cancer spreads, you may experience bone pain, headaches, or yellowing of the skin if it reaches the liver. Tell your doctor about any new or worsening symptoms.
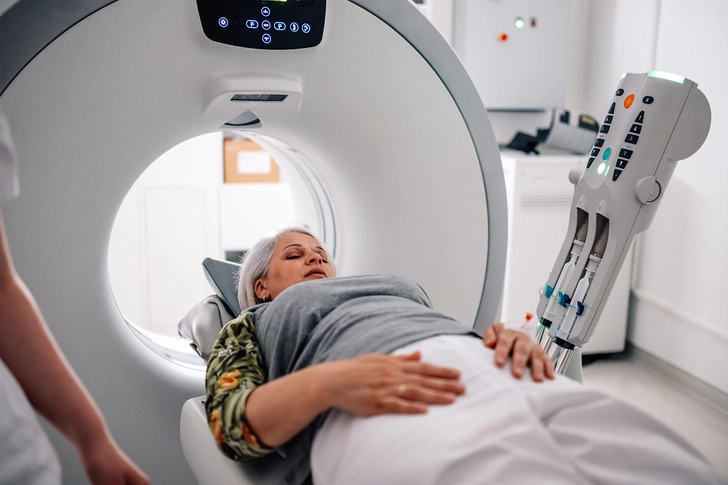
Diagnosing Stage IV NSCLC
Your doctor may order imaging scans like CT, PET, or MRI to locate tumors and determine the extent of cancer spread. A biopsy, where a small tissue sample is taken, helps confirm the diagnosis and identify specific cancer type. Blood tests can check overall health and detect certain proteins that may indicate cancer. These tests help create a comprehensive picture of your condition.

Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a key treatment for stage IV NSCLC. This approach uses drugs that target specific genetic mutations in cancer cells. Your doctor will perform genetic testing on your tumor to determine if you're a candidate. Targeted therapies can be effective in slowing cancer growth and managing symptoms with fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
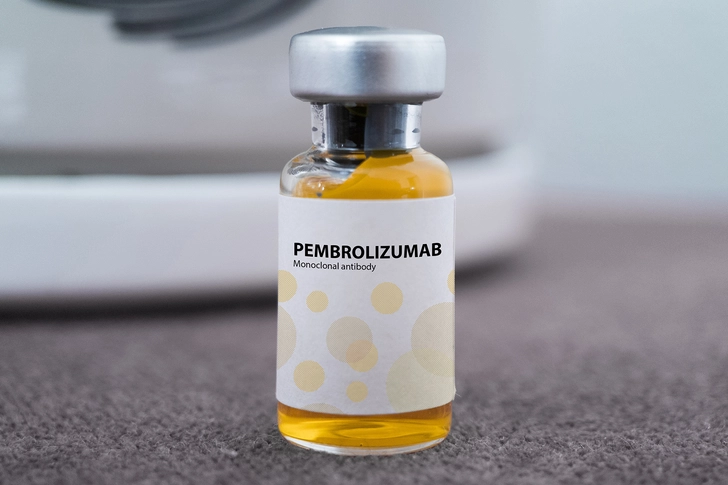
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is another important treatment. This approach boosts your immune system to fight cancer cells. Drugs called checkpoint inhibitors, such as nivolumab or pembrolizumab, can be effective in some patients. Your doctor may test your tumor for PD-L1 protein levels to determine if immunotherapy is suitable for you. This treatment can help shrink tumors and help you live longer in some cases.
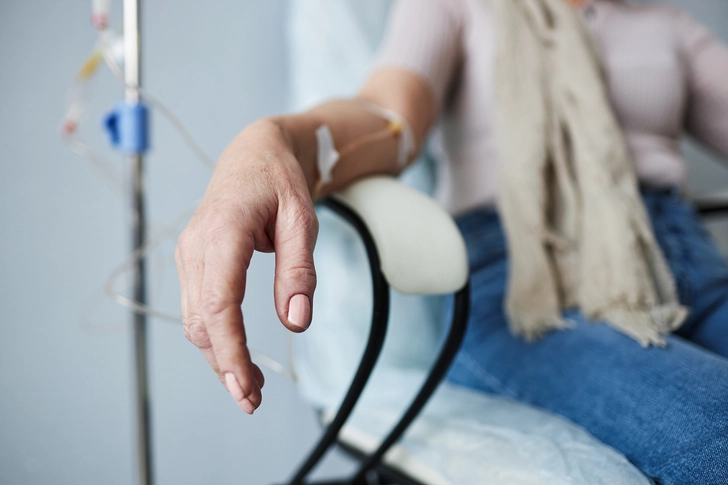
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy remains a standard treatment for many people with this type of cancer. It uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. While it can be effective in controlling cancer growth and symptoms, it may cause side effects like fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. Your doctor may combine chemotherapy with other treatments like immunotherapy for better results. The specific drugs and schedule depend on your overall health and cancer characteristics.
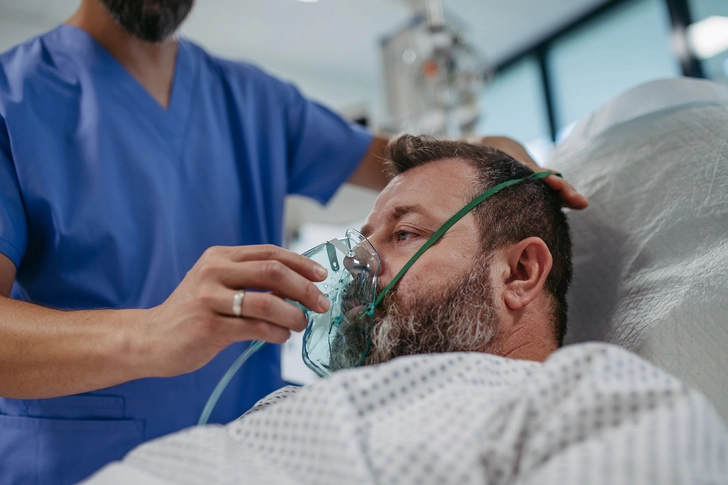
Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on improving quality of life by managing symptoms and side effects. It can include pain management, respiratory support, and emotional counseling. Palliative care works alongside other treatments to ensure you're comfortable and able to maintain the best possible quality of life.
PHOTO CREDITS:
Slide 1: New Africa/Shutterstock
Slide 2: Photoroyalty/Shutterstock
Slide 3: Zamrznuti tonovi/Shutterstock
Slide 4: Mongkolchon Akesin/Shutterstock
Slide 5: Sonis Photography/Shutterstock
Slide 6: SeventyFour/Shutterstock
Slide 7: Halfpoint/Shutterstock
SOURCES:
Cancer Metastasis Reviews: "Progression and Metastasis of Lung Cancer."
Chest: "Treatment of Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer."
American Cancer Society: "Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Signs and Symptoms," "Tests Used on Biopsy and Cytology Specimens to Diagnose Cancer," "Treating Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer," "Immunotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer."
Mayo Clinic: "Lung Cancer."
Johns Hopkins Medicine: "Am I a Candidate for Lung Transplant?"
American Lung Association: "Supportive (Palliative) Care for Lung Cancer."