- Headaches Overview
- Migraine
- Cluster & Tension Headaches
- Other Types of Headaches
- Appointment Prep
- View Full Guide
High-Frequency Episodic Migraines

What Are High-Frequency Episodic Migraines?
Migraine is a neurological disorder in which you get recurring severe headaches. High-frequency episodic migraines (HFEM) involve migraine attacks occurring 10 to 14 times per month. The intensity and frequency of migraine attacks can vary from person to person and can worsen over time.

Risk Factors
Approximately 12% of Americans have migraine. Women are three times more likely to experience migraines, especially those aged 15 to 55. Other risk factors include family history, stress, smoking, and obesity. Certain medical conditions like head injuries and asthma can also worsen migraine frequency and severity.

Common Triggers
Hormonal changes, bright lights, loud noises, strong smells, sleep disturbances, and dietary factors are common migraine triggers. Using pain relievers too frequently can cause medication overuse headaches.
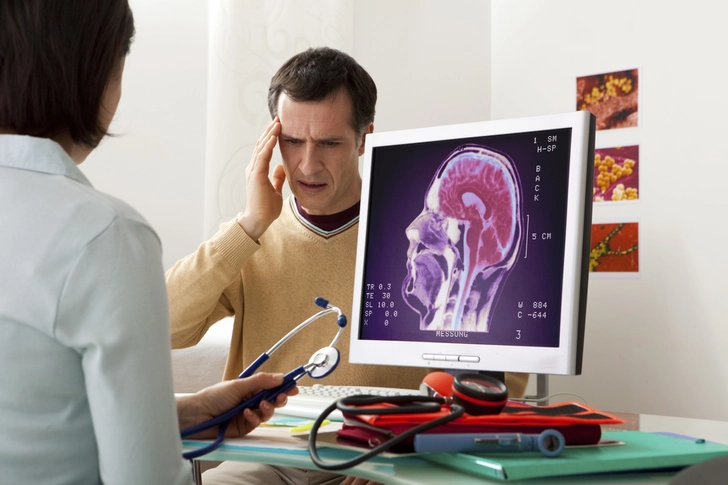
Diagnosing HFEM
Diagnosis involves tracking headache patterns and discussing symptoms with your doctor. Your doctor may also order tests to rule out other conditions. Keeping a migraine journal to track your symptoms can help you get a diagnosis.
While there's no cure for migraine, various treatments can help, including over-the-counter medications like aspirin and ibuprofen, prescription drugs like triptans and beta-blockers, and lifestyle changes.

Lifestyle Management
Regular sleep, hydration, meals, and exercise help prevent migraine attacks. Stress management techniques and avoiding known triggers are equally important.

Quality of Life and Progression
If you’re having frequent migraine attacks or if they're getting worse, tell your doctor as soon as possible. They can help you find the right treatment plan to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
PHOTO CREDITS:
Slide 1 - peterschreiber.media / Shutterstock
Slide 2 - Juliya Shangarey / Shutterstock
Slide 3 - Shopping King Louie / Shutterstock
Slide 4 - Image Point Fr / Shutterstock
Slide 5 - Inside Creative House / Shutterstock
Slide 6 - Studio Romantic / Shutterstock
SOURCES:
Cleveland Clinic: “Migraine Headaches.”
Medlineplus.gov: “Migraine.”
American Migraine Foundation: “Are You at Risk for Chronic Migraine?" “Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS) for Acute Migraine Treatment.”
Current Pain and Headache Reports: “Defining the Differences Between Episodic Migraine and Chronic Migraine.”
The Journal of Headache and Pain: “Shift from high-frequency to low-frequency episodic migraine in patients treated with Galcanezumab: results from two global randomized clinical trials,” “The impact of headache in Europe: principal results of the Eurolight project.”
Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain: “Migraine Burden of Disease: From the Patient's Experience to a Socio-Economic View.”
Headaches.org: “The Migraine Disability Assessment Test.”