- Headaches Overview
- Migraine
- Cluster & Tension Headaches
- Other Types of Headaches
- Appointment Prep
- View Full Guide
What Is an Occipital Nerve Block?

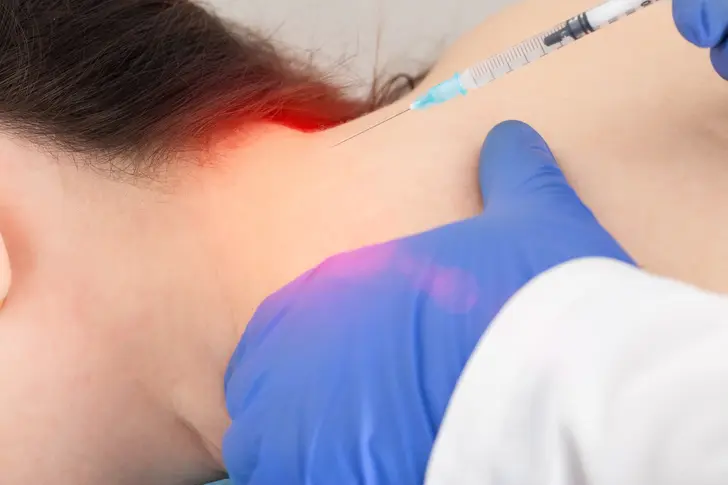
What Is an Occipital Nerve Block?
An occipital nerve block is a procedure where your doctor injects a combination of pain medicine and steroids into the scalp, at the back of your head. This is usually done to treat chronic headaches.
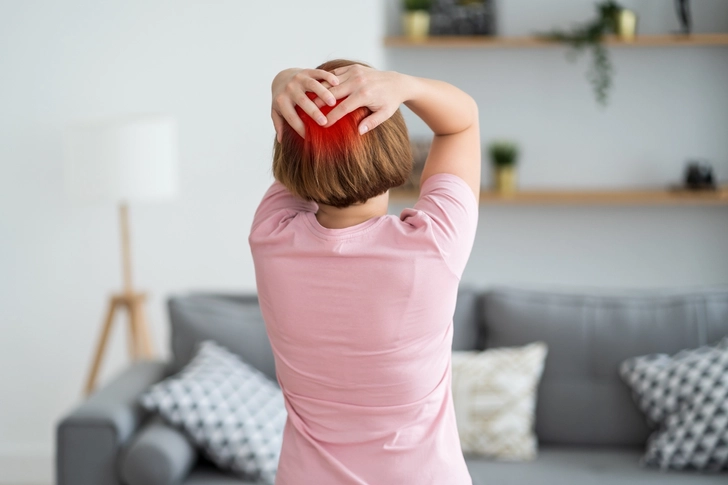

Who Might Benefit?
This treatment works best for people with certain types of headaches, especially those that cause pain at the back of the head. It's particularly helpful for occipital neuralgia (nerve pain) and some types of migraines.
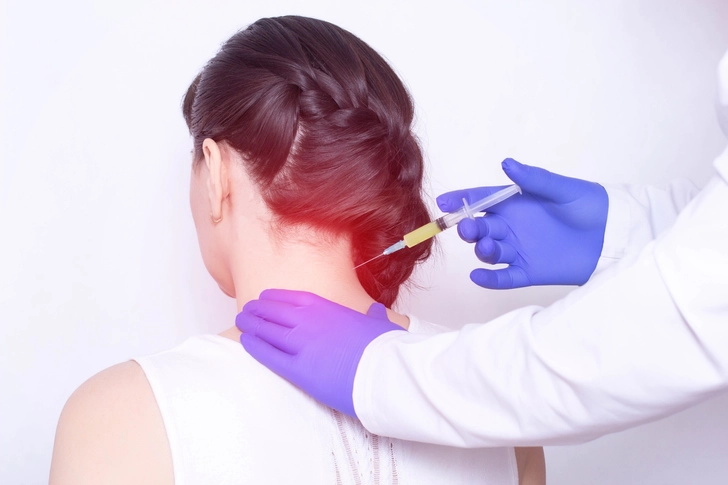
Procedure Details
The procedure takes only about 5-10 minutes and is done in a doctor's office. You'll sit or lie down while the doctor gives you a few small injections at the base of your skull where the occipital nerves are located.
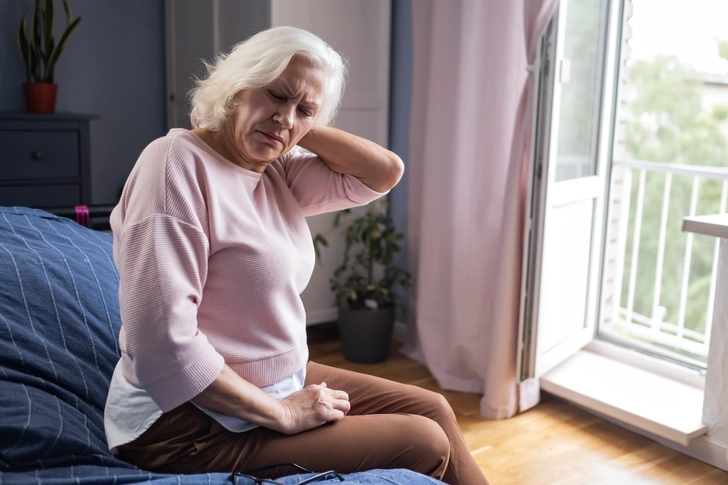

How Long Relief Lasts
Most people feel relief within 15 minutes as the numbing medication takes effect. You might notice temporary numbness at the back of your head or a warm, tingling feeling that spreads across your scalp. The immediate numbing effect wears off after several hours, but the pain relief from the steroid can last much longer. Some people get relief for weeks or even months after a single treatment.
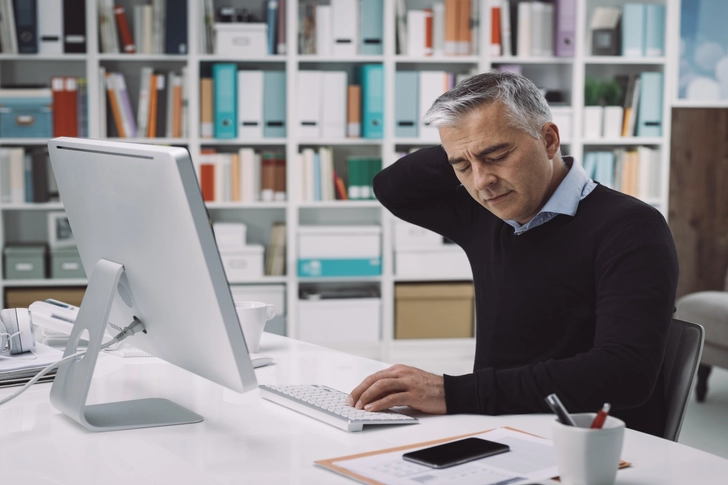


Multiple Treatments
If the first nerve block works well but wears off, you can usually get repeat treatments. Many doctors recommend waiting at least three months between steroid injections to lessen side effects from the steroid.
PHOTO CREDENTIALS
Slide 1 - HenadziPechan/Shutterstock
Slide 2 - staras/Shutterstock
Slide 3 - HenadziPechan/Shutterstock
Slide 4 - Koldunov/Shutterstock
Slide 5 - Stock-Asso/Shutterstock
Slide 6 - Nor Gal/Shutterstock
SOURCES:
American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine: "Overview of Occipital Neuralgia and Greater Occipital Nerve Blocks."
Lifespan Health System: "Occipital Nerve Block."
Mayo Clinic: "Cluster headaches."
Stanford Health Care: "Occipital Nerve Block."
UCI Health: "Occipital Nerve Block."
Headache: "Expert Consensus Recommendations for the Performance of Peripheral Nerve Blocks for Headaches – A Narrative Review."
StatPearls: "Occipital Nerve Block," "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Occipital Nerves."
Cleveland Clinic: "Occipital Nerve Block," "Cervicogenic Headache."
Royal College of Anaesthetists: "Nerve damage associated with peripheral nerve block."