- Overview
- Types
- Hormonal Methods
- Barrier Methods
- Behavioral Methods
- Medical Methods
- Male Birth Control
- Emergency Contraception
- Side Effects & Complications
- View Full Guide
What is Depo-Provera?

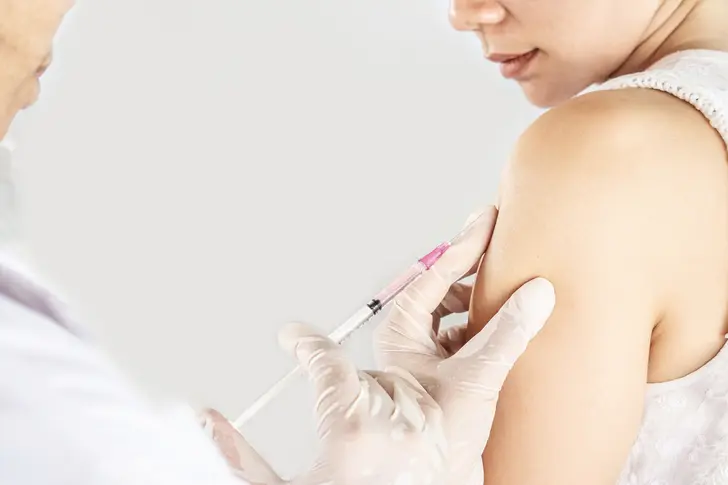
What Is Depo-Provera?
Depo-Provera is birth control method you can get as a shot. It's a man-made hormone, medroxyprogesterone, which is similar to the natural hormone progesterone.

How Does It Work?
Depo-Provera stops the ovaries from releasing eggs and alters the uterine lining and cervical mucus to keep sperm from reaching any eggs.
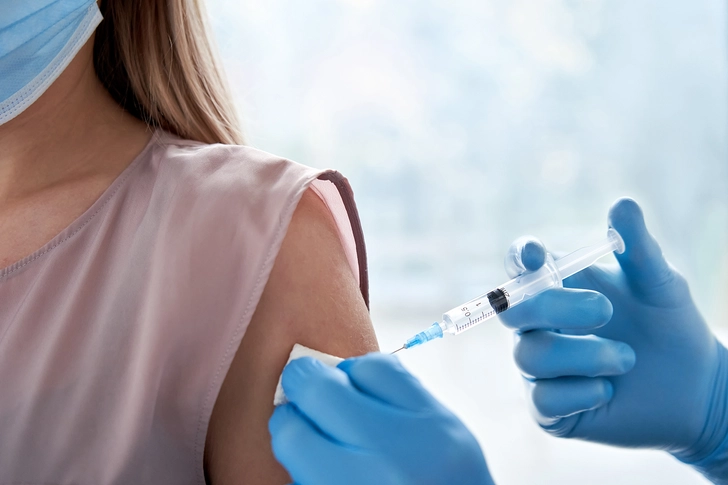
How to Use
You'll have to get a shot every 12 weeks to get full protection. After your first injection, doctors recommend using backup birth control, such as a condom, for the first 7 days.

Common Side Effects
Changes to your menstrual cycle are the most common side effects. After a year of use, about 50% of women will stop getting their periods. Other common side effects include headaches, weight gain, and acne.
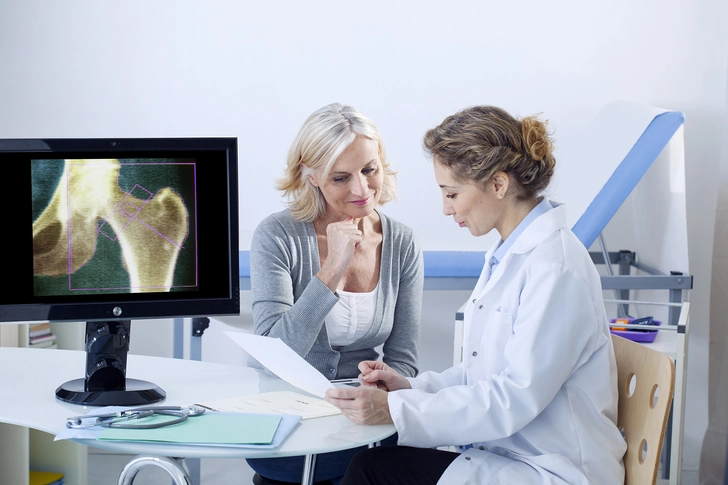
Bone Mineral Density Concerns
Long-term use of Depo-Provera may lead you to lose bone mineral density, which makes you more likely to get osteoporosis. Your chances are higher if you've taken the shot for longer than 2 years, especially if osteoporosis runs in your family, if you drink a lot, if you smoke, or if you have other risk factors for the condition.

Who Should Not Use Depo-Provera?
People with certain medical conditions should avoid using Depo-Provera. These include liver disease, breast cancer, and blood clots.

STD Protection
Depo-Provera does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). If you are at risk of STDs, consider using additional protection, such as condoms.
Photo Credits:
1) Doucefleur/Shutterstock
2) Shutterstock
3) Ground Picture/Shutterstock
4) Millana/Shutterstock
5) Image Point Fr/Shutterstock
6) Shutterstock
7) Pixel-Shot/Shutterstock
SOURCES:
FamilyDoctor.org: "Depo-Provera: An Injectable Contraceptive."
MedlinePlus: "Medroxyprogesterone Injection."
Sexuality Information and Education Council of the United States: "Talk About Sex."
Center for Young Women's Health: “Depo-Provera® Hormonal Injections.”
Mayo Clinic: “Depo-Provera (contraceptive injection).”
Nationwide Children’s: “Birth Control: The Shot (Depo-Provera).”
Cleveland Clinic: “Depo-Provera.”
CDC: “Contraception: Birth Control Methods,” “Update to U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use: Self-Administration of Subcutaneous Depot Medroxyprogesterone Acetate.”
New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority: “Medroxyprogesterone and withdrawal syndrome.”
Nemours/KidsHealth: “The Birth Control Shot.”
Kaiser Family Foundation: “DMPA Contraceptive Injection: Use and Coverage.”
Reproductive Health Access Project: “Contraceptive Pearl: Self-Administered Progestin Injection: Depo SubQ.”
UpToDate: “Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA): Efficacy, side effects, metabolic impact, and benefits.”
Pfizer: “DEPO-SUBQ PROVERA- medroxyprogesterone acetate injection, suspension.”