What Are Uterine Polyps?

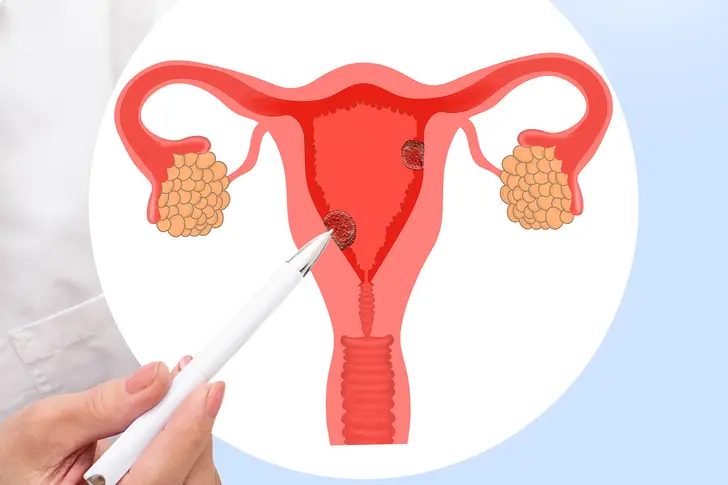
What Are Uterine Polyps?
Uterine polyps are small, soft growths that form on the lining of the uterus. Sizes can range from as small as a sesame seed to as large as a golf ball.

Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause is unknown but is linked to changes in hormones, especially estrogen. Risk factors include age (40-50), obesity, high blood pressure, and use of tamoxifen (a breast cancer medication).

Common Symptoms
Symptoms can vary. Some women have no symptoms, especially if they have small polyps or only one polyp. Other women may experience irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding, bleeding between periods, vaginal bleeding after menopause, and fertility issues.
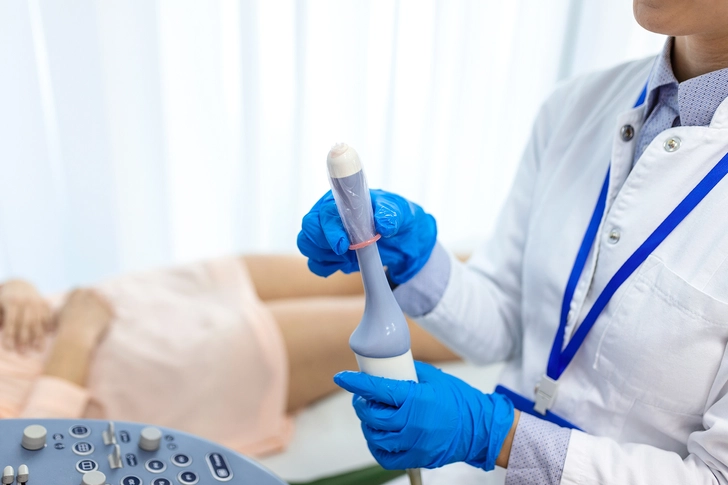
Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosis involves procedures such as transvaginal ultrasound, hysterosonography, hysteroscopy, endometrial biopsy, and curettage. These methods help visualize and sample the polyps for analysis.
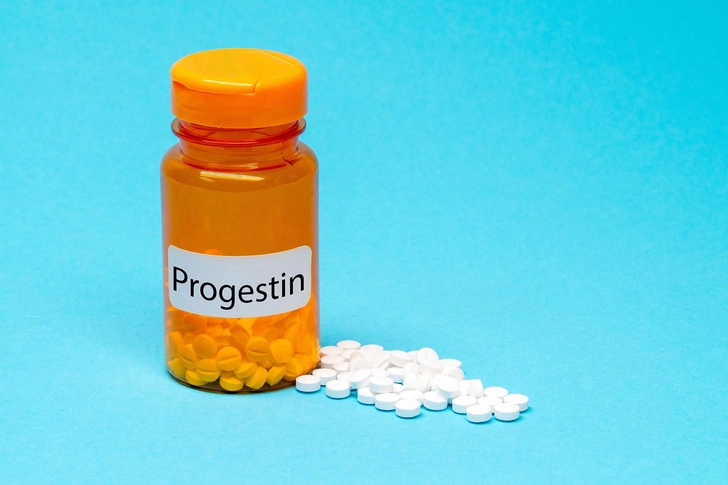
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on symptoms and overall health. Options include watchful waiting, hormonal therapies such as progestins, and surgical removal via hysteroscopy or curettage. In rare cases, a hysterectomy may be needed if cancer is detected.

Prevention Tips
There is no sure way to prevent uterine polyps, but maintaining a healthy weight may reduce the risk. Regular checkups are essential for women with a history of polyps to watch for recurrence.
PHOTO CREDITS:
Slide 1: Peakstock/Shutterstock
Slide 2: New Africa/Shutterstock
Slide 3: Doucefleur/Shutterstock
Slide 4: Photoroyalty/Shutterstock
Slide 5: luchschenF/Shutterstock
Slide 6: Pixel-Shot/Shutterstock
SOURCES:
Baylor College of Medicine: "Endometrial Polyps."
Mayo Clinic: "Uterine Polyps," "Uterine Fibroids."
Cleveland Clinic: "Uterine Polyps."
The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist.
Loma Linda University Center for Infertility: "Uterine Polyps."
Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology.
Fibroid Treatment Collective: "Uterine Polyps vs. Fibroids."
Surgery Research and Practice: "Surgical Management of Endometrial Polyps in Infertile Women: A Comprehensive Review."
University of Colorado Gynecologic Oncology: "Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps)," "Uterine Fibroids, Endometrial Polyps and Ovarian Cysts."
ColumbiaDoctors: "Uterine Polyps."