- Overview
- Types
- Symptoms
- Causes & Risks
- Tests & Diagnosis
- Treatment
- Living With
- Mobility & Assistive Devices
- Complications
- Caregiving & Support
- Appointment Prep
- View Full Guide
Disease-Modifying Drugs for MS
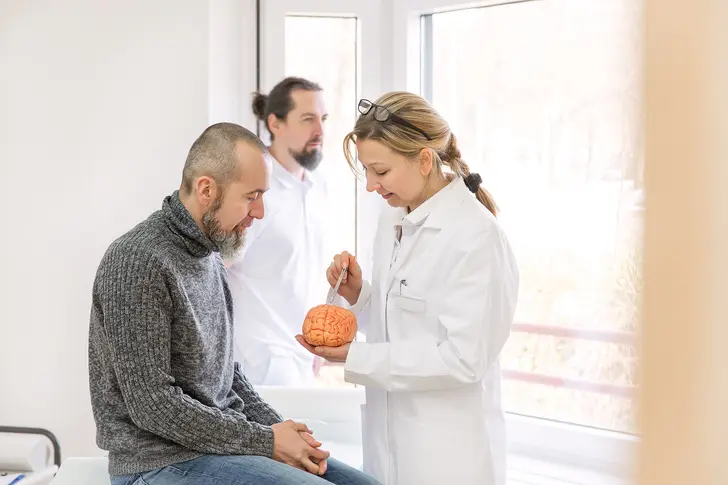


What Are Disease-Modifying Drugs?
Disease-modifying drugs slow down MS by holding back or changing how your body's immune system works. MS happens because your immune system attacks the coating around your nerves, called myelin. These medications don't cure MS, but they lower the number of attacks, make them less severe, and prevent new brain lesions.
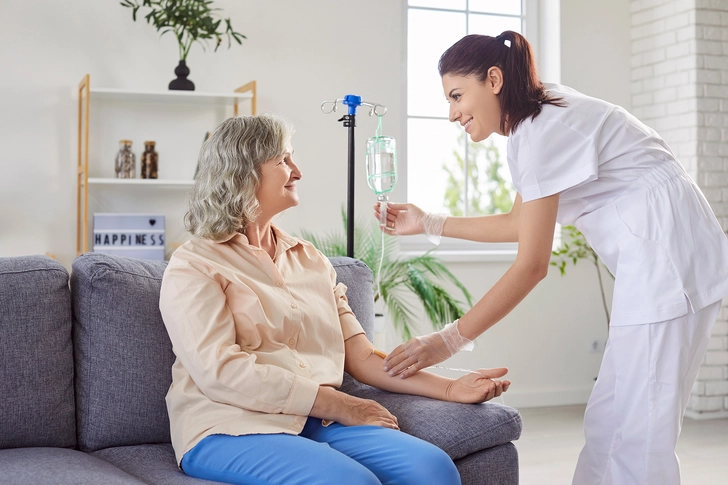


Kesimpta (Ofatumumab)
Kesimpta treats relapsing forms of MS, CIS, RRMS, and active secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. You get it by injection, with the first three doses given one week apart, then maintenance doses every four weeks. Common side effects include fever, chills, and fatigue.
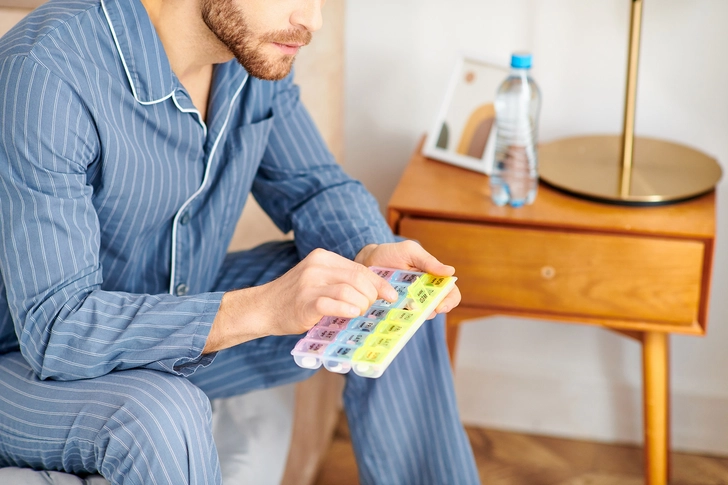

Mayzent (Siponimod)
Mayzent treats clinically isolated syndrome plus relapsing and secondary progressive forms of MS. You take it as a pill by mouth daily. Common side effects include headaches, high blood pressure, and liver damage.

Aubagio (Teriflunomide)
Aubagio treats relapsing forms of MS. You take it as a tablet by mouth daily. Common side effects include diarrhea, liver problems, nausea, and hair loss.
Tecfidera (Dimethyl Fumarate)
Tecfidera treats relapsing forms of MS. You take it as a pill by mouth twice daily. Common side effects include flushing, stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
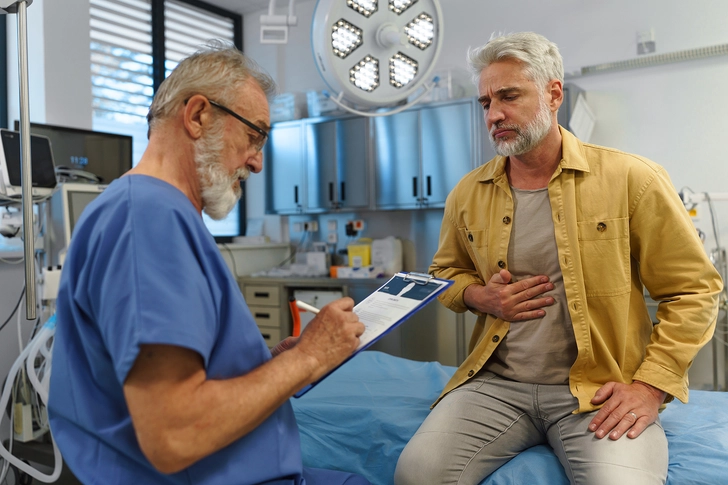

Vumerity (Diroximel Fumarate)
Vumerity treats relapsing forms of MS, CIS, RRMS, and active secondary progressive MS. You take it as a pill by mouth, starting with one pill twice daily the first week, then two pills twice daily afterward. Common side effects include flushing, stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash.

Gilenya (Fingolimod)
Gilenya treats relapsing MS. You take it as a pill by mouth daily. Common side effects include headache, diarrhea, back pain, and abnormal liver tests.

Zeposia (Ozanimod)
Zeposia treats relapsing forms of MS, CIS, RRMS, and active secondary progressive MS. You take it by mouth as a capsule once daily. Common side effects include upper respiratory infection, urinary tract infection, drop in blood pressure when you stand, high blood pressure, increased liver enzymes, and back pain.
Mavenclad (Cladribine)
Mavenclad treats relapsing and secondary progressive forms of MS (but not clinically isolated syndrome). You take it as a pill by mouth for four to five days, then four to five days about a month later. After one year, this is repeated. Common side effects include headaches, low white blood cell counts, and infections.
Tysabri (Natalizumab)
Tysabri treats relapsing forms of MS. You get it through an IV infusion every four weeks. Common side effects include headache, feeling tired, and joint pain.

Lemtrada (Alemtuzumab)
Lemtrada treats relapsing forms of MS. You get it through an IV infusion for five days in a row, then three days in a row a year later. Common side effects include rash, headache, fever, stuffy nose, nausea, and joint pain.

Plegridy (Peginterferon Beta-1a)
Plegridy treats relapsing forms of MS. You take it once every two weeks as an injection in prefilled pens or prefilled syringes. The dose should be increased in two-week steps until the full dose is reached after four weeks. Common side effects include a reaction where the needle entered your skin and flu-like symptoms.
Rebif (Interferon Beta-1a)
Rebif treats relapsing forms of MS. You take it by injection under the skin three times per week. Common side effects include mild flu-like symptoms and a reaction where the needle entered the skin.

Avonex (Interferon Beta-1a)
Avonex treats relapsing forms of MS and is also given after an initial episode of symptoms (Clinically isolated syndrome). You take it by injection into a muscle weekly. Common side effects include mild flu-like symptoms and a reaction where the needle entered the skin.

Betaseron (Interferon Beta-1b)
Betaseron treats relapsing forms of MS. You take it by injection under the skin every other day. Common side effects include mild flu-like symptoms.

Copaxone/Glatopa (Glatiramer Acetate)
Glatiramer acetate treats relapsing-remitting MS. You take it by injection under the skin three times per week. Common side effects include a skin reaction where the needle went in and weakness.

Novantrone (Mitoxantrone)
Novantrone is rarely used for rapidly worsening relapsing-remitting MS and for progressive relapsing or secondary progressive forms of MS. You get it through an IV infusion every three months or four times a year for a total of eight to 12 doses. Common side effects include nausea, hair thinning, and decreased white blood cell count.

Bafiertam (Monomethyl Fumarate)
Bafiertam treats relapsing forms of MS, CIS, RRMS, and active secondary progressive MS. You take it as a capsule by mouth twice a day. Common side effects include flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, PML, lymphopenia, anaphylaxis/angioedema, and liver injury.

Choosing Your MS Treatment
Your doctor will probably suggest you start taking one as soon as you're diagnosed with relapsing-remitting MS. Things to consider include side effects, benefits, how often you take them, how you take them, and your personal concerns, priorities, and lifestyle. The goal is to find a treatment you can use comfortably and consistently.
PHOTO CREDENTIALS
Slide 01 - Miriam Doerr Martin Frommherz / Shutterstock
Slide 02 - Studio Romantic / Shutterstock
Slide 03 - AYO Production / Shutterstock
Slide 04 - LightField Studios / Shutterstock
Slide 05 - Kimberly Boyles / Shutterstock
Slide 06 - Kristen Prahl / Shutterstock
Slide 07 - Halfpoint / Shutterstock
Slide 08 - Kong AP / Shutterstock
Slide 09 - Lysenko Andrii / Shutterstock
Slide 10 - Kosoff / Shutterstock
Slide 11 - SeventyFour / Shutterstock
Slide 12 - Dmytro Zinkevych / Shutterstock
Slide 13 - Zetaphotostudio / Shutterstock
Slide 14 - Sergii Gnatiuk / Shutterstock
Slide 15 - Babul Hosen / Shutterstock
Slide 16 - H_Ko / Shutterstock
Slide 17 - Nuttawut Uttamaharad / Shutterstock
Slide 18 - SeventyFour / Shutterstock
Slide 19 - Ground Picture / Shutterstock
Slide 20 - fizkes / Shutterstock
SOURCES:
Biogen Idec.
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
FDA.
National MS Society: “Ocrevus.”
Prescribers' Digital Reference: “Avonex (interferon beta-1a),” ”Rebif (interferon beta-1a),” “Tecfidera (dimethyl fumarate).”
Mayo Clinic: “Glatiramer (Subcutaneous Route).”